Computer - Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Central Processing Unit
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit; it is also known as “the brain of the computer”. A CPU is a primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing and controls the operation of all components running inside a computer.
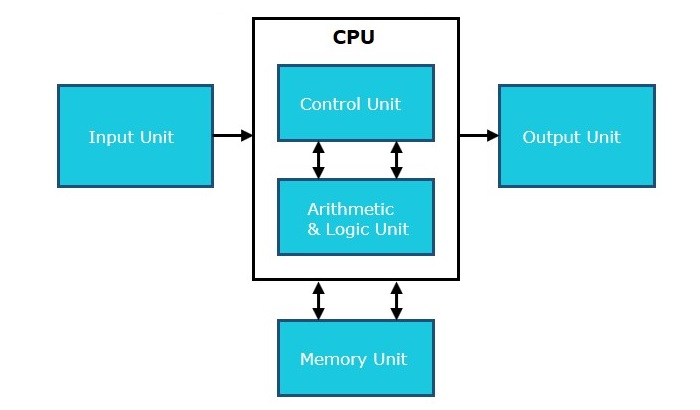
The key components of a CPU are the Control Unit, ALU and Memory. The alignment and integration of key components are included in the above figure.
Components of CPU
- Control Unit (CU)
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- Memory or Storage Unit
- Registers
Control Unit
As its name implies, a control unit acts as the “brain” of the CPU. A major role of a control unit is to manage and execute instructions to perform the tasks specified by a computer program. v. A CPU executes instructions by fetching them from memory, decodes them, and then executes them. So, it plays a vital role in fetch-decode-execute instructions.
Functions of Control Unit
- Instruction Fetch − A CU fetches instructions from RAM (Random Access Memory).
- Instruction Decoding − It decodes the fetched instructions to operate.
- Instruction Execution − A CU sends control signals to perform operations like ALU for arithmetic and logical operations.
- Control Flow Management − It controls flow by updating the programme counter.
- Exception Handling − A control unit effectively manages exceptions and interruptions like hardware failures, system calls, and external events, by appropriately diverting the control flow of the CPU to the planned procedure for managing such exceptions.
- Synchronization − A CU plays a crucial role in facilitating the coordination of instruction execution across several cores.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a component that has been extensively optimised and engineered to do multiple tasks concurrently. It is commonly built to execute operations speedily. It works in conjunction with other CPU components, such as registers, memory, and control units, to execute complex instructions.
Functions of an ALU
- Arithmetic Operations − The ALU can perform basic arithmetic operations.
- Logic Operations − The ALU can also perform logical operations like AND, OR, NOT, XOR, and bit-shifting operations.
Memory Unit
A memory is a hardware component which is used to store and access the data whenever required. Majorly; computer memory is categorised into two parts Primary Memory (RAM) and Secondary Memory (Hard Disk). RAM is used for short-term, fast data access and is essential for active program execution. On the other hand, storage or secondary memory provides permanent data storage.
Hence, memory and storage units both are critical components of a computer system.
Functions of memory
Primary Memory
- RAM is also known as primary or temporary memory; it is a type of volatile memory used for temporarily storing data.
- The contents inside the RAM are erased when the computer’s power gets off or restarted.

- RAM is actively used for program or instruction execution.
- Once we start the computer; system necessary files, programs and operating system files are loaded into the RAM for the smooth running of the computer.
- The more RAM a computer has, the better it can handle multitasking and the faster it can run applications since data can be accessed more quickly.
Storage (Hard Drives, SSDs, Flash Drives, etc.)
- Storage devices are used to store the data permanently, even when the computer is powered off.
- They are non-volatile; the data remains intact even when the power is turned off or the system restarts.

- The most popular and commonly used storage devices are Hard disks (HDs), Solid-State Drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, and optical disks (e.g., DVDs), pen drives.
- The data storage capacity of these devices in gigabytes (GB) to terabytes (TB) and more, depending on the type and size of the storage device.
Functions of the CPU
The key functions of a CPU are as follows −
- The CPU performs arithmetic and logic operations.
- It directs the operation of the processor.
- It directs Input and output units that how to respond to the instructions that have been communicated to the processor.
- A CPU contains registers which are considered small storage locations within the CPU to hold data temporarily during execution of a program.
- A CPU executes instructions by fetching them from memory, decodes them, and then executes them.