Classification of Computers
A computer can be classified based on its size, capacity, and purpose. The following diagram illustrates different types of computers as per their size, capacity, and purpose.
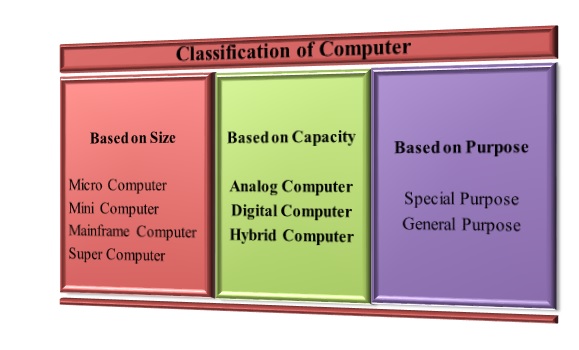
Computer’s classification based on Size
As per the size, a computer can be broadly classified as follows −
- Micro Computer
- Mini Computer
- Mainframe Computer
- Super Computer
Micro Computer
Microcomputers, also known as personal computers (PCs), are a type of computer designed for individual use. They are distinguished by their compact dimensions, small size, processing power, compatibility, internet connectivity, portability, low price, and versatility. In the 1970s and 1980s, microcomputers gained popularity and became more popular in the modern computing era.

Fig: Micro Computer
-
Size − Microcomputers are small in size. These are portable.
-
Example − Some of the popular microcomputers are laptops and desktops, standard PCs, mobile phones, and notebooks.
-
Why microcomputer ?
Microcomputers have become an important part of modern life. They have had a big impact on society, companies, education, and related areas.
-
Uses of Microcomputers − Microcomputers are most widely used in education and learning, entertainment and media, innovation and creativity, research and science, healthcare and medicine, home automation, remote work, and e-commerce and online shopping.
Minicomputer
A minicomputer is a type of computer that is smaller in size than large computers. It possesses all the capabilities of a large computer. Hence, it is a midsize multi-processing system capable of supporting up to 250 users simultaneously.

Fig: Mini Computer
- Size − Its size falls between mainframes and microcomputers. It is larger than mainframe computers and smaller than microcomputers.
- Example − Some of the popular minicomputers are the PDP-11, IBM’s AS/400e, Honeywell 200, and TI-990.
- Why a Mini Computer? Mini computers are also known as mini PCs or small-form-factor (SFF) computers. These have impressive computing capabilities, high performance, connectivity options, portability, and versatility features.
- Uses of Minicomputers − Minicomputers are most widely used in scientific computations, engineering, business transaction processing, file handling, and database management.
Mainframe computer
The mainframe is very large and is an expensive computer capable of supporting hundreds or even thousands of users simultaneously. The mainframe executes many programmes concurrently and supports simultaneous execution of programmes.

Fig: Mainframe Computer
-
Size − Mainframe computers can vary in size; their size generally depends on their specifications and the specific model being considered.
-
Example − Some of the popular mainframe computers are IBM zSeries mainframes (BM z14 and IBM z15), Unisys ClearPath, Fujitsu GS21 Series, and Hitachi VOS3.
-
Why a mainframe computer?
The processing capacity of mainframes is frequently measured in MIPS (million instructions per second) or other units. This enables them to process a large volume of transactions and perform extensive data processing.
-
Uses of the Mainframe − Mainframe computers are most widely used in finance, government, healthcare, and more.
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a special type of computer that is more powerful and capable of high-performance computing. It is specifically designed to compute complex and intensive tasks that regular computers cannot do efficiently.
- Size − Supercomputers can vary in size, from small clusters of computers to massive installations. A supercomputer may contain 10, 100, 1000, or more computers that all work together.

Fig: Super Computer
- Example − Some of the popular supercomputers are Fugaku, Google Sycamore, Baidu’s quantum supercomputer, and Sierra.
- Why Supercomputer?
- A supercomputer’s processing speed is exceptional and can perform billions of calculations per second. Multiple processors work in parallel mode to execute tasks, which makes processing powerful.
- Supercomputers are specially built using specialised hardware like GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) or TPUs (Tensor Processing Units), which are used in graphics rendering or machine learning tasks.
- Supercomputers represent the pinnacle of computing power, and these are very expensive and are employed for specialised applications.
- Uses of the Supercomputer − Supercomputers are most widely used in scientific research, data analysis, weather forecasting, scientific simulations, graphics, fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, electronic design, and the analysis of geological data.
Computer’s classification based on Capacity
As per the capacity, a computer can be broadly classified as follows −
- Analog Computer
- Digital computer
- Hybrid computer
Analog Computer
A computer that uses physical means like mechanical or hydraulic components to do the computation rather than electronic circuits is called an analogue computer. These computers work with continuous data and can manage physical quantities efficiently. They are particularly good at solving differential equations and simulating dynamic systems.

Fig: Analog computer
In lieu of numbers, an analogue computer performs arithmetic operations based on measurable quantities, such as mechanical movement or the rotation of gears. In analogue computers, data is processed as continuous signals for its operation, whereas in digital computers, data is transmitted as discrete signals (or discontinuous signals).
Digital Computer
A digital computer is a type of computer that represents and processes data using discrete, distinct values.

Fig: Digital computer
In digital computers, data is processed using binary numbers 0 and 1. These computers are designed to perform arithmetic calculations and complex data processing and manipulation. The main components of a digital computer are input, processing, and output.
Hybrid Computer
A hybrid computer is a type of computer system that integrates the features and capabilities of both analogue and digital computers. This integration allows the hybrid computer to perform various tasks efficiently by leveraging the strengths of both digital and analogue technologies.
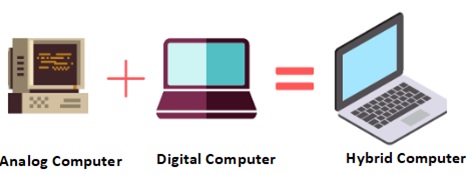
Fig: Hybrid computer
The main components of a hybrid computer are the analogue and digital components −
- Analog Component − Analogue components in a hybrid computer can process real-world data like voltage, current, temperature, pressure, etc. using analogue circuits and components.
- Digital Component − Digital computers work with discrete data and are based on binary numbers (0s and 1s). Digital components in a hybrid computer provide the computational power to perform complex calculations and control the overall operation of the system.
Computer’s classification based on Purpose
As per the capacity, a computer can be broadly classified as follows −
- Special Purpose
- General Purpose
Special Purpose Computer
A computer that is designed and optimised for a specific task or set of tasks is called a special purpose computer (SPC). SPCs are designed to excel at a single or limited set of functions, frequently with a high degree of efficiency, speed, and accuracy.

Fig: Special Purpose Computer
Some of the following popular SPCs are:
- Embedded Systems − These systems are integrated with devices to control specific functions. For example, a car’s engine control unit and microwave ovens
- Digital Signal Processors − These are commonly used in applications like audio processing, image compression, and telecommunications.
- Automated Teller Machines − ATMs are special-purpose computers designed specifically for banking transactions and interactions with customers.
- Medical Equipment − Machines like MRI and CT scanners are specialised computers used for capturing and processing medical images.
- Spacecraft Computers − Computers used in spacecraft have to operate in extreme conditions and are optimised for the demands of space missions.
General Purpose Computer
A computer that is designed to perform a wide range of tasks and functions is called A General Purpose Computer (GPC). A GPC is versatile and can be used for various purposes by running different software and applications.

Fig: General Purpose Computer
Some of the following popular GPCs are as −
- Turing Completeness − A GPC can simulate any algorithm or computation that can be explored algorithmically.
- Programmability − GPCs can run different applications.
- General-Purpose Operating System − GPCs like Windows, macOS, or Linux that provide an interactive user interface and manage hardware resources, enabling the execution of various application programmes.
- Input and Output Capabilities − GPCs have input and output devices (keyboard, mouse, monitor, etc.) that permit users to interact with the system and receive feedback.