Computer - Generations
The development of computers has gone through different generations, each generation marked by significant advancements in terms of technology and architecture. These generations are classified as follows:
- First generation
- Second generation
- Third generation
- Fourth generation
- Fifth generation
First Generation
- The timeline for the first generation computers was 1940 to 1956.
- The first generation computers were developed using vacuum tube or thermionic valve machine.
- Punched cards and paper tape were used as input/output.
- Magnetic drums and magnetic tapes were used as a memory device to save the data.

- These computers were consuming lot of electricity because of vacuum tubes and other electronic devices and generate lot of heat.
- These were bigger in size and more expensive.
- These computers were worked on binary-coded concept (i.e., language of 0-1).
- Examples − ENIAC, EDVAC, etc.
Second Generation
- The timeline for the second generation computers was 1956 to 1963.
- Transistors were used to develop.
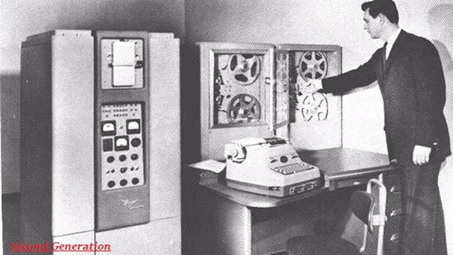
- In comparison to the first generation, second generation computers were small in size.
- Punched cards and magnetic tape were used for input /output.
- Electricity consumption was low and produces less heat.
- Magnetic core memory was used.
- Fast computing and were used in business, scientific research, and government applications.
- Examples − UNIVAC, IBM 1401, IBM 7090.
Third Generation
- The timeline for the third generation computers was 1963 to 1971.
- Integrated Circuit (IC) was used to develop.
- In comparison to the second generation, third generation computers were small in size.
- Magnetic tape, keyboard, monitor, printer devices were used as input and output.

- Computation power was higher as compare to second generation computers.
- The third generation computer consumed less power and also generated less heat.
- The maintenance cost of the computers in the third generation was also low as these were consuming less power and generated less heat.
- These were most widely used in commercial purposes.
- Examples − UNIVAC, IBM 360, IBM 370.
Fourth Generation
- The timeline for the fourth generation computers was 1972 to 2010.
- Microprocessor technology was used to develop.
- These were surprising in terms of size and computing power.

-
Portable computers.
-
Very less power consuming and affordable.
-
Semiconductor memory such as RAM, ROM were used which makes computation faster.
-
Keyboard, pointing devices, optical scanning, monitor, printer devices were used for input and output.
-
It became available for the common people as well.
-
Examples − IBM PC, STAR 1000, Apple.
Fifth Generation
- The timeline for the fifth generation computers is form 2010 to till date.
- These computers are based on artificial intelligence, Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI), Quantum computation, Nanotechnology, Parallel processing technology.

- Very fast and multiple tasks could be performed simultaneously.
- These are smaller in size as compare to fourth generation computers.
- Consumes very low power.
- Keyboard, monitor, mouse, touchscreen, scanner, printer are used as an input output devices.
- Examples − Laptops, tablets, smartphones are most popular examples of fifth generation computers.