CSS Background
In this tutorial you will learn how to define background styles for an element using CSS.
Setting Background Properties
Background plays an important role in the visual presentation of a web page.
CSS provide several properties for styling the background of an element, including coloring the background, placing images in the background and managing their positioning, etc.
The background properties are background-color, background-image, background-repeat, background-attachment and background-position.
In the following section we will discuss each of these properties in more detail.
Background Color
The background-color property is used to set the background color of an element.
The following example demonstrates how to set the background color of the whole page.
Example
body {
background-color: #f0e68c;
}
Color values in CSS are most often specified in the following formats:
- a color name - like “red”
- a HEX value - like “#ff0000”
- an RGB value - like “rgb(255, 0, 0)“
Background Image
The background-image property set an image as a background of an HTML element.
Let’s check out the following example which sets the background image for the whole page.
Example
body {
background-image: url("images/tile.png");
}
Note: When applying the background image to an element, make sure that the image you choose does not affect the readability of the element’s text content.
Tip: By default browser repeats or tiles the background image both horizontally and vertically to fill the entire area of an element. You can control this with
background-repeatproperty.
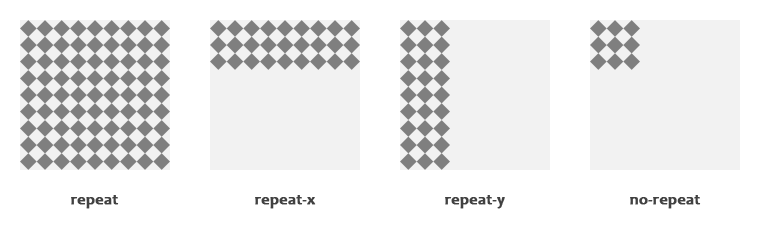
Background Repeat
The background-repeat property allows you to control how a background image is repeated or tiled in the background of an element. You can set a background image to repeat vertically (y-axis), horizontally (x-axis), in both directions, or in neither direction.
Let’s try out the following example which demonstrates how to set the gradient background for a web page by repeating the sliced image horizontally along the x-axis.
Example
body {
background-image: url("images/gradient.png");
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
Similarly, you can use the value repeat-y to repeat the background image vertically along the y-axis, or the value no-repeat to prevent the repetition altogether.
Example
body {
background-image: url("images/texture.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
Let’s take a look at the following illustration to understand how this property actually works.
Background Position
The background-position property is used to control the position of the background image.
If no background position has been specified, the background image is placed at the default top-left position of the element i.e. at (0,0), let’s try out the following example:
Example
body {
background-image: url("images/robot.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
In the following example, the background image is positioned at top-right corner.
Example
body {
background-image: url("images/robot.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
}
Note: If two values are specified for the
background-positionproperty, the first value represents the horizontal position, and the second represents the vertical position. If only one value is specified, the second value is assumed to be center.
Besides keywords, you can also use percentage or length values, such as px or em for this property.
Let’s take a look at the following illustration to understand how this property actually works.
p.one {
color: #0000ff;
border: 2px solid;
}
p.two {
color: #00ff00;
outline: 2px solid;
}
Background Attachment
The background-attachment property determines whether the background image is fixed with regard to the viewport or scrolls along with the containing block.
Let’s try out the following example to understand how it basically works:
Example
body {
background-image: url("images/bell.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
}
The Background Shorthand Property
As you can see in the examples above, there are many properties to consider when dealing with the backgrounds. However, it is also possible to specify all these properties in one single property to shorten the code or avoid extra typing. This is called a shorthand property.
The background property is a shorthand property for setting all the individual background properties, i.e., background-color, background-image, background-repeat, background-attachment and the background-position property at once. Let’s see how this works:
Example
body {
background-color: #f0e68c;
background-image: url("images/smiley.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-position: 250px 25px;
}
Using the shorthand notation the above example can be written as:
Example
body {
background: #f0e68c url("images/smiley.png") no-repeat fixed 250px 25px;
}
When using the background shorthand property the order of the property values should be.
background: color image repeat attachment position;
If the value for an individual background property is missing or not specified while using the shorthand notation, the default value for that property will be used instead, if any.
h1, h2, h3 { font-weight: normal;}h1 { font-size: 36px;}h2 { font-size: 28px;}h3 { font-size: 22px;}css