Python if-else Statement
Python if else Statement
The if-else statement in Python is used to execute a block of code when the condition in the if statement is true, and another block of code when the condition is false.
Syntax of if-else Statement
The syntax of an if-else statement in Python is as follows −
if boolean_expression:
# code block to be executed
# when boolean_expression is true
else:
# code block to be executed
# when boolean_expression is false
If the boolean expression evaluates to TRUE, then the statement(s) inside the if block will be executed otherwise statements of the else block will be executed.
Flowchart of if-else Statement
This flowchart shows how if-else statement is used −
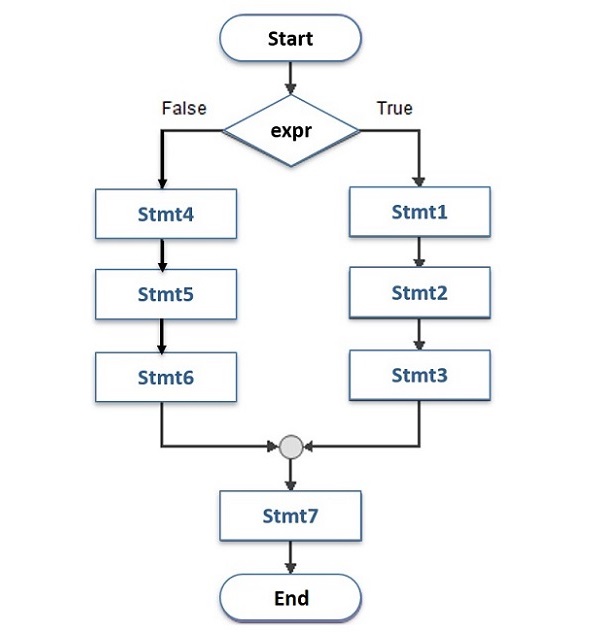
If the expr is True, block of stmt1, 2, 3 is executed then the default flow continues with stmt7. However, if the expr is False, block stmt4, 5, 6 runs then the default flow continues.
Python implementation of the above flowchart is as follows −
if expr==True:
stmt1
stmt2
stmt3
else:
stmt4
stmt5
stmt6
Stmt7
Python if-else Statement Example
Let us understand the use of if-else statements with the following example. Here, variable age can take different values. If the expression age > 18 is true, then eligible to vote message will be displayed otherwise not eligible to vote message will be displayed. Following flowchart illustrates this logic −
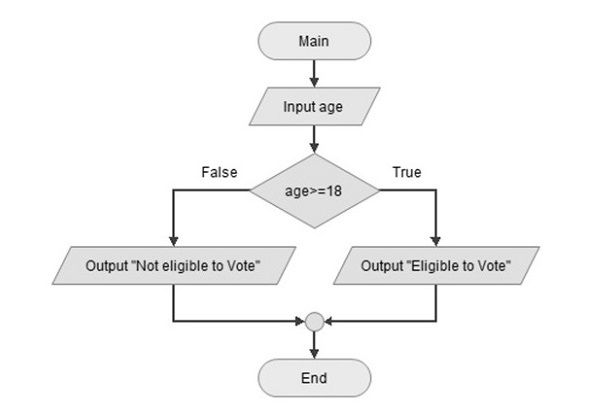
Now, let’s see the Python implementation the above flowchart.
age=25
print ("age: ", age)
if age >=18:
print ("eligible to vote")
else:
print ("not eligible to vote")
On executing this code, you will get the following output −
age: 25
eligible to vote
To test the else block, change the age to 12, and run the code again.
age: 12
not eligible to vote
Python if elif else Statement
The if elif else statement allows you to check multiple expressions for TRUE and execute a block of code as soon as one of the conditions evaluates to TRUE.
Similar to the else block, the elif block is also optional. However, a program can contains only one else block whereas there can be an arbitrary number of elif blocks following an if block.
Syntax of Python if elif else Statement
if expression1:
statement(s)
elif expression2:
statement(s)
elif expression3:
statement(s)
else:
statement(s)
How if elif else Works?
The keyword elif is a short form of else if. It allows the logic to be arranged in a cascade of elif statements after the first if statement. If the first if statement evaluates to false, subsequent elif statements are evaluated one by one and comes out of the cascade if any one is satisfied.
Last in the cascade is the else block which will come in picture when all preceding if/elif conditions fails.
Example
Suppose there are different slabs of discount on a purchase −
- 20% on amount exceeding 10000,
- 10% for amount between 5-10000,
- 5% if it is between 1 to 5000.
- no discount if amount<1000
The following flowchart illustrates these conditions −
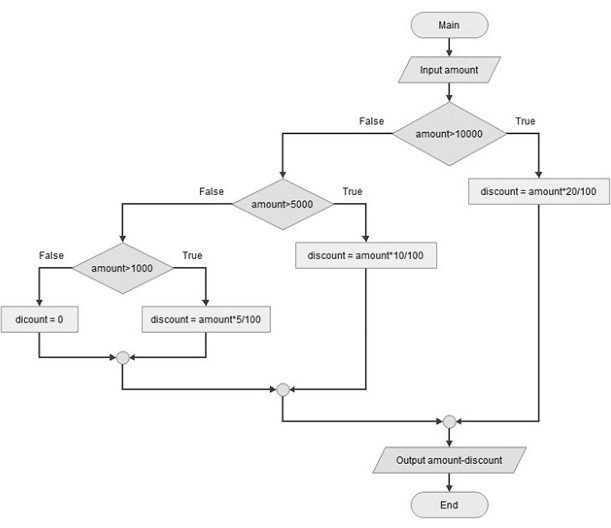
We can write a Python code for the above logic with if-else statements −
amount = 2500
print('Amount = ',amount)
if amount > 10000:
discount = amount * 20 / 100
else:
if amount > 5000:
discount = amount * 10 / 100
else:
if amount > 1000:
discount = amount * 5 / 100
else:
discount = 0
print('Payable amount = ',amount - discount)
Set amount to test all possible conditions: 800, 2500, 7500 and 15000. The outputs will vary accordingly −
Amount: 800
Payable amount = 800
Amount: 2500
Payable amount = 2375.0
Amount: 7500
Payable amount = 6750.0
Amount: 15000
Payable amount = 12000.0
While the code will work perfectly fine, if you look at the increasing level of indentation at each if and else statement, it will become difficult to manage if there are still more conditions.
Python if elif else Statement Example
The elif statement makes the code easy to read and comprehend. Following is the Python code for the same logic with if elif else statements −
amount = 2500
print('Amount = ',amount)
if amount > 10000:
discount = amount * 20 / 100
elif amount > 5000:
discount = amount * 10 / 100
elif amount > 1000:
discount = amount * 5 / 100
else:
discount=0
print('Payable amount = ',amount - discount)
The output of the above code is as follows −
Amount: 2500
Payable amount = 2375.0