Python - While Loops
A while loop in Python programming language repeatedly executes a target statement as long as the specified boolean expression is true. This loop starts with while keyword followed by a boolean expression and colon symbol (:). Then, an indented block of statements starts.
Here, statement(s) may be a single statement or a block of statements with uniform indent. The condition may be any expression, and true is any non-zero value. As soon as the expression becomes false, the program control passes to the line immediately following the loop.
If it fails to turn false, the loop continues to run, and doesn’t stop unless forcefully stopped. Such a loop is called infinite loop, which is undesired in a computer program.
Syntax of while Loop
The syntax of a while loop in Python programming language is −
while expression:
statement(s)
In Python, all the statements indented by the same number of character spaces after a programming construct are considered to be part of a single block of code. Python uses indentation as its method of grouping statements.
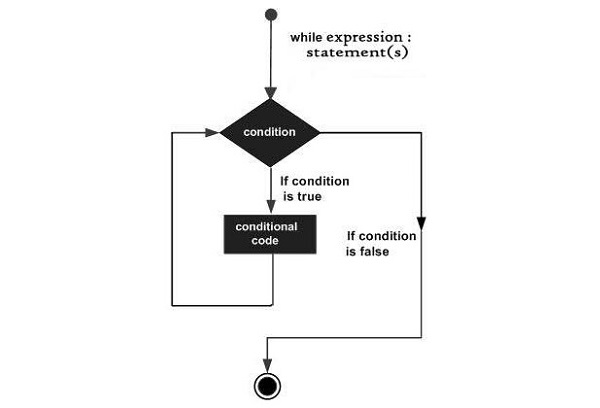
Flowchart of While loop
The following flow diagram illustrates the while loop −
Example 1
The following example illustrates the working of while loop. Here, the iteration run till value of count will become 5.
count=0
while count<5:
count+=1
print ("Iteration no. {}".format(count))
print ("End of while loop")
On executing, this code will produce the following output −
Iteration no. 1
Iteration no. 2
Iteration no. 3
Iteration no. 4
Iteration no. 5
End of while loop
Example 2
Here is another example of using the while loop. For each iteration, the program asks for user input and keeps repeating till the user inputs a non-numeric string. The isnumeric() function returns true if input is an integer, false otherwise.
var = '0'
while var.isnumeric() == True:
var = "test"
if var.isnumeric() == True:
print ("Your input", var)
print ("End of while loop")
On running the code, it will produce the following output −
enter a number..10
Your input 10
enter a number..100
Your input 100
enter a number..543
Your input 543
enter a number..qwer
End of while loop
Python Infinite while Loop
A loop becomes infinite loop if a condition never becomes FALSE. You must be cautious when using while loops because of the possibility that this condition never resolves to a FALSE value. This results in a loop that never ends. Such a loop is called an infinite loop.
An infinite loop might be useful in client/server programming where the server needs to run continuously so that client programs can communicate with it as and when required.
Example
Let’s take an example to understand how the infinite loop works in Python −
var = 1
while var == 1 : # This constructs an infinite loop
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
print ("You entered: ", num)
print ("Good bye!")
On executing, this code will produce the following output −
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number :11
You entered: 11
Enter a number :22
You entered: 22
Enter a number :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "examples\test.py", line 5, in
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
KeyboardInterrupt
The above example goes in an infinite loop and you need to use CTRL+C to exit the program.
Python while-else Loop
Python supports having an else statement associated with a while loop. If the else statement is used with a while loop, the else statement is executed when the condition becomes false before the control shifts to the main line of execution.
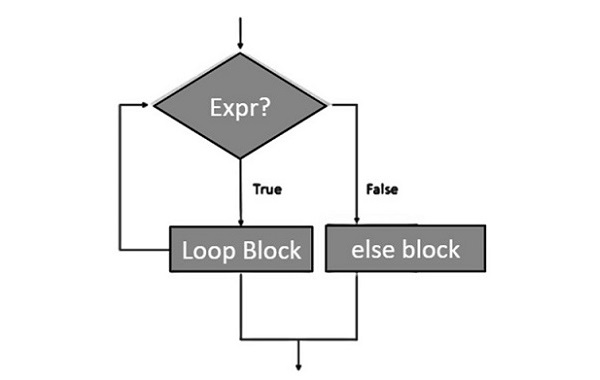
Flowchart of While loop with else Statement
The following flow diagram shows how to use else statement with while loop −
Example
The following example illustrates the combination of an else statement with a while statement. Till the count is less than 5, the iteration count is printed. As it becomes 5, the print statement in else block is executed, before the control is passed to the next statement in the main program.
count=0
while count<5:
count+=1
print ("Iteration no. {}".format(count))
else:
print ("While loop over. Now in else block")
print ("End of while loop")
On running the above code, it will print the following output −
Iteration no. 1
Iteration no. 2
Iteration no. 3
Iteration no. 4
Iteration no. 5
While loop over. Now in else block
End of while loop
Single Statement Suites
Similar to the if statement syntax, if your while clause consists only of a single statement, it may be placed on the same line as the while header.
Example
The following example shows how to use one-line while clause.
flag = 0
while (flag): print ("Given flag is really true!")
print ("Good bye!")
When you run this code, it will display the following output −
Good bye!
Change the flag value to “1” and try the above program. If you do so, it goes into infinite loop and you need to press CTRL+C keys to exit.