Python - String Concatenation
String concatenation in Python is the operation of joining two or more strings together. The result of this operation will be a new string that contains the original strings. The diagram below shows a general string concatenation operation −
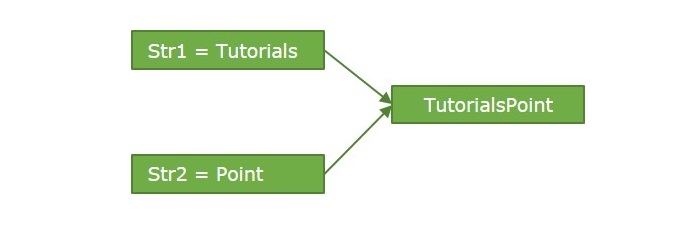
In Python, there are numerous ways to concatenate strings. We are going to discuss the following −
- Using ’+’ operator
- Concatenating String with space
- Using multiplication operator
- Using ’+’ and ’*’ operators together
String Concatenation using ’+’ operator
The ”+” operator is well-known as an addition operator, returning the sum of two numbers. However, the ”+” symbol acts as string concatenation operator in Python. It works with two string operands, and results in the concatenation of the two.
The characters of the string on the right of plus symbol are appended to the string on its left. Result of concatenation is a new string.
Example
The following example shows string concatenation operation in Python using + operator.
str1="Hello"
str2="World"
print ("String 1:",str1)
print ("String 2:",str2)
str3=str1+str2
print("String 3:",str3)
It will produce the following output −
String 1: Hello
String 2: World
String 3: HelloWorld
Concatenating String with space
To insert a whitespace between two strings, we can use a third empty string.
Example
In the below example, we are inserting space between two strings while concatenation.
str1="Hello"
str2="World"
blank=" "
print ("String 1:",str1)
print ("String 2:",str2)
str3=str1+blank+str2
print("String 3:",str3)
It will produce the following output −
String 1: Hello
String 2: World
String 3: Hello World
String Concatenation By Multiplying
Another symbol _, which we normally use for multiplication of two numbers, can also be used with string operands. Here, _ acts as a repetition operator in Python. One of the operands must be an integer, and the second a string. The integer operand specifies the number of copies of the string operand to be concatenated.
Example
In this example, the * operator concatenates multiple copies of the string.
newString = "Hello" * 3
print(newString)
The above code will produce the following output −
HelloHelloHello
String Concatenation With ’+’ and ’*’ Operators
Both the repetition operator () and the concatenation operator (+), can be used in a single expression to concatenate strings. The "" operator has a higher precedence over the ”+” operator.
Example
In the below example, we are concatenating strings using the + and * operator together.
str1="Hello"
str2="World"
print ("String 1:",str1)
print ("String 2:",str2)
str3=str1+str2*3
print("String 3:",str3)
str4=(str1+str2)*3
print ("String 4:", str4)
To form str3 string, Python concatenates 3 copies of World first, and then appends the result to Hello
String 3: HelloWorldWorldWorld
In the second case, the strings str1 and str2 are inside parentheses, hence their concatenation takes place first. Its result is then replicated three times.
String 4: HelloWorldHelloWorldHelloWorld
Apart from + and *, no other arithmetic operators can be used with string operands.